Laser cutting is a versatile and efficient method of processing a wide range of materials. This includes metals such as aluminum. Despite its widespread use, people often question the effectiveness and efficiency of laser cutting aluminum. This is due to its unique properties. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the process. It also covers the advantages and challenges of laser cutting aluminum.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a technique that uses a high-powered laser beam to cut precise patterns and shapes into materials. It is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system. This makes it highly accurate and repeatable. Laser cutting works by focusing a laser beam onto the surface of a material. The laser melts, burns, or vaporizes the material. This process leaves a clean, sharp edge.
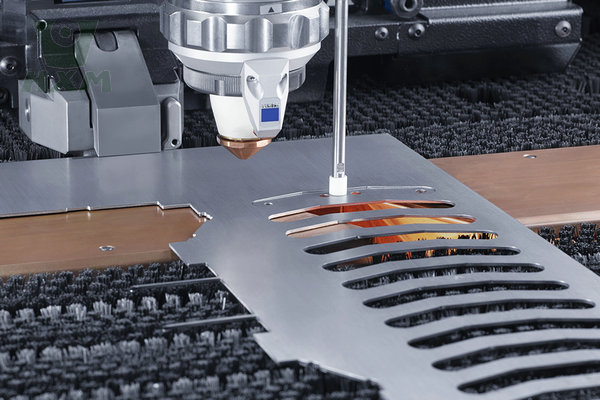

How Laser Cutting Works?
By following these steps, laser cutting can provide a precise, efficient method for cutting a variety of materials.
Process Steps | Description | More Information |
Laser Power Generation | A laser source produces a concentrated beam of light. | The laser source can be CO2, fiber, or Nd, depending on the material and precision required. |
Focusing | The beam is focused onto the surface of the material by a lens. | The lens focuses the laser to a fine point, increasing the intensity of the beam on a specific area of the material. |
Melting/Vaporization | The intense heat from the laser causes the material to melt or vaporize. | The heat from the laser is enough to melt or vaporize the material, thus creating the cut. |
Cutting Path | The CNC system controls the movement of the laser head, guiding it along the desired cutting path. | The Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system ensures precision and repeatability in cutting complex shapes and patterns. |
Laser Types Used
Utilizing the most advanced laser cutting technologies including CO2, Fiber Optic, and Ndlasers, we provide precise, efficient cutting solutions tailored to your specific needs.
| Laser Types | Applications | More Information |
| CO2 Lasers | Non-metallic materials, some metals adjusted | Great for materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, and some plastics. – Can cut metals such as steel and aluminum with the proper settings. |
| Fiber Lasers | Metals, including aluminum | Efficient in cutting metals. – Known for high cutting speeds and low maintenance. |
| Neodymium Lasers | Cutting and Welding | Suitable for cutting and welding a wide range of materials. – Commonly used in industries that require precision, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. |
Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are generally more effective at cutting aluminum than CO2 lasers. Their wavelengths are more easily absorbed by metals, including aluminum, and are therefore able to cut thicker and more reflective metals.
CO2 Lasers
Although CO2 lasers are not as efficient at cutting aluminum as fiber lasers, they can still be used with modifications, such as increasing the power setting or using a “pulsed” mode to minimize the heat affected zone.
Can Aluminum be Cut with a Laser?
Yes, aluminum can be laser cut. However, this requires understanding its specific properties and how they interact with laser technology. Aluminum is known for its light weight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutting Solution?
Aluminum Sheet thickness ≤ 3 mm → Fiber laser 2 kW + compressed air
Aluminum Sheet thickness 3 – 6 mm → Fiber laser 4 kW + nitrogen
Aluminum Plate thickness > 6 mm → Fiber laser 6 kW or mixed gas (O₂ + N₂)
Consult Huaxiao Metal now to get exclusive process parameter tables and cost calculations
Challenges of Laser Cutting Aluminum
By addressing these challenges with the proper strategies and equipment, high-quality aluminum laser cutting can be achieved.
Reflectivity
Aluminum is highly reflective, especially to the infrared light of a CO2 laser. This reflectivity can present a challenge because it can reflect the laser beam out of the material, making the cutting process less efficient.
Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, meaning it dissipates heat quickly. This is a problem for laser cutting because it can result in uneven cuts and require a more powerful laser.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the aluminum can affect the quality of the cut. Thicker aluminum requires higher laser power or a different type of laser to achieve a clean cut.
Oxidation
When cutting aluminum, the aluminum forms an oxide layer that can interfere with the laser-cutting process. This oxidation can result in poor cut quality and may require additional cleaning or preparation steps.

Need professional help? Contact our technical team for custom cutting parameters.
How to Improve Aluminum Laser Cutting Efficiency
Improving aluminum laser cutting efficiency involves optimizing various factors related to the laser equipment, material preparation, and cutting parameters. Here are some strategies to improve aluminum laser cutting efficiency:
Use the Right Laser Parameters
Adjusting the power, speed, and focal length of the laser is critical to accommodate the unique properties of aluminum. The best settings depend on the thickness and type of aluminum being cut.
Protective Coatings
Applying a protective coating to the aluminum helps absorb the laser light and reduce reflectivity. These coatings can be temporary and are removed after the cutting process is complete.
Proper Material Support
Properly supporting the aluminum on the cutting table ensures stability and precision during the cutting process. Using honeycomb or slatted supports minimizes reflections and improves cut quality.
Gas Assist
Using assist gases such as nitrogen or oxygen can help improve the cutting process. Nitrogen prevents oxidation and makes for cleaner cuts, while oxygen increases cutting speeds.

At Huaxiao Metal, we not only supply high-quality aluminum alloy products but also offer custom laser cutting services to meet diverse project needs.
Applications of Laser Cut Aluminum
Laser cutting aluminum can be used in a variety of applications that require precision and flexibility. These applications include:
Aerospace
For lightweight and delicate parts. Aluminum’s strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for aerospace applications where reducing weight without compromising strength is critical.
Automotive
When manufacturing components, reducing weight is critical. Laser cutting can produce complex shapes and designs that improve the efficiency and performance of automotive parts.
Electronics
For delicate conductive components. Aluminum’s excellent conductivity makes it a popular choice for electronic applications ranging from circuit boards to heat sinks.
Signage and Decoration
Due to its beauty and durability, laser cutting aluminum can be used for intricate designs in signage, artwork, and decorations, presenting a sleek and modern look.
Aluminum is used in architecture for both structural and decorative purposes. Laser cutting allows for the precision required for custom architectural elements and accessories.
Medical Devices
The medical industry utilizes aluminum to manufacture equipment and devices due to its non-reactive nature and precision cutting capabilities. Laser cutting can be used to manufacture complex medical devices and components.

If your project requires precision and durability, laser cutting aluminum can fit the bill, contact us today for a custom quote.
Advantages of Laser Cutting Aluminum
Why do we choose laser cutting of aluminum?
Laser cutting aluminum offers numerous advantages that make it the method of choice for a variety of industrial and manufacturing applications. Here are some of the key advantages:
Advantages | Description |
Platform Accuracy | Allows highly detailed cuts and complex designs. |
Speed | Faster than many traditional mechanical cutting techniques. |
Highly Flexible | Can be easily reprogrammed to accommodate different designs and configurations. |
Low Thermal Shock | Minimizes heat-affected zone, preserving aluminum’s properties. |
Efficiency | High efficiency and low waste make this a cost-effective cutting method. |
Clean Edges | Produces clean, burr-free edges, reducing the need for additional finishing operations. |
Platform Precision
Laser cutting offers unparalleled precision. This allows for the creation of complex designs and detailed patterns. This is especially important in industries where precision is critical. Examples include the aerospace and electronics industries.
Speed
Laser cutting is much faster than many traditional mechanical cutting methods. This speed translates to higher productivity. It also allows for faster turnaround times. This makes it an attractive option for high-volume manufacturing.
Highly Flexible
One of the key benefits of laser cutting is its flexibility. The process can be easily adapted to different designs and configurations. This allows for rapid prototyping and customization. All without extensive retooling.
Low Heat Impact
Laser cutting minimizes the heat-affected zone (HAZ), helping to preserve the properties of aluminum. This is critical for applications where the strength and integrity of the material need to be maintained.
Efficiency
Laser cutting is highly efficient and produces minimal material waste. The precision of the process ensures that only necessary material is removed, which reduces waste and saves costs.
Clean Edges
Laser cutting produces clean, burr-free edges, often requiring little additional finishing. This reduces the need for secondary operations and helps streamline production.
If you’re looking for aluminum alloy for sale, or want to combine purchase with laser cutting services, we’re here to help.
In Conclusion
Laser cutting is a practical and effective aluminum cutting method. However, it presents specific challenges due to the properties of the metal. By choosing the right laser type. Adjusting the cutting parameters. and properly preparing the material. Manufacturers can efficiently and effectively use lasers to cut aluminum for a wide range of applications.
As the technology advances, the process will become even more efficient. This will open up new possibilities for aluminum used in a variety of industries in China. For more information and professional CNC machining services, please contact us directly!